How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional pilots. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety regulations to advanced flight techniques and camera operation. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, navigation strategies, and essential maintenance procedures, ensuring you’re well-equipped to handle your drone with confidence and expertise.
Understanding these elements is vital for capturing stunning aerial footage and ensuring responsible operation within legal and ethical guidelines.
We will delve into the specifics of different drone models and their unique functionalities, providing practical tips and troubleshooting advice to help you overcome common challenges. From mastering smooth takeoffs and landings to optimizing battery life and managing drone footage, this guide serves as your comprehensive resource for becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient drone operation. This involves inspecting various drone components and adhering to established safety regulations. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be performed before every flight. This ensures all systems are functioning correctly and minimizes the risk of accidents.
| Component | Check | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or secure attachment. | Replace damaged propellers immediately. | |
| Battery | Check battery level, voltage, and condition. Ensure proper connection. | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. | |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality, lens clarity, and gimbal stability. | Clean the lens if necessary. | |
| GPS and Compass | Confirm GPS signal strength and compass calibration. | Recalibrate if necessary. A weak signal may necessitate a flight delay. | |
| Radio Control System | Check the controller’s battery level and ensure a strong connection with the drone. | Test all control sticks and buttons. | |
| Airframe | Inspect the drone’s body for any damage or loose parts. | Report and address any issues before flight. |
Essential Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation demands strict adherence to safety regulations and best practices. These rules are designed to protect both the operator and the surrounding environment.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering people or property.
- Check weather conditions before each flight and avoid flying in adverse weather.
- Be aware of local regulations and obtain necessary permits.
Flight Delay/Cancellation Decision-Making Process
Weather and other unforeseen circumstances may necessitate delaying or cancelling a drone flight. A clear decision-making process is vital for ensuring safety.
A flowchart would visually represent the decision points, starting with checking weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation, visibility). If conditions are unfavorable (exceeding safe limits), the flight is cancelled. If conditions are favorable, proceed to the pre-flight checklist. If any issues arise during the checklist, the flight is delayed or cancelled. If all checks pass, the flight can commence.
A final check for airspace restrictions would also be included before initiating flight.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation

Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the function of typical drone controls and navigation modes.
Drone Remote Control Functions
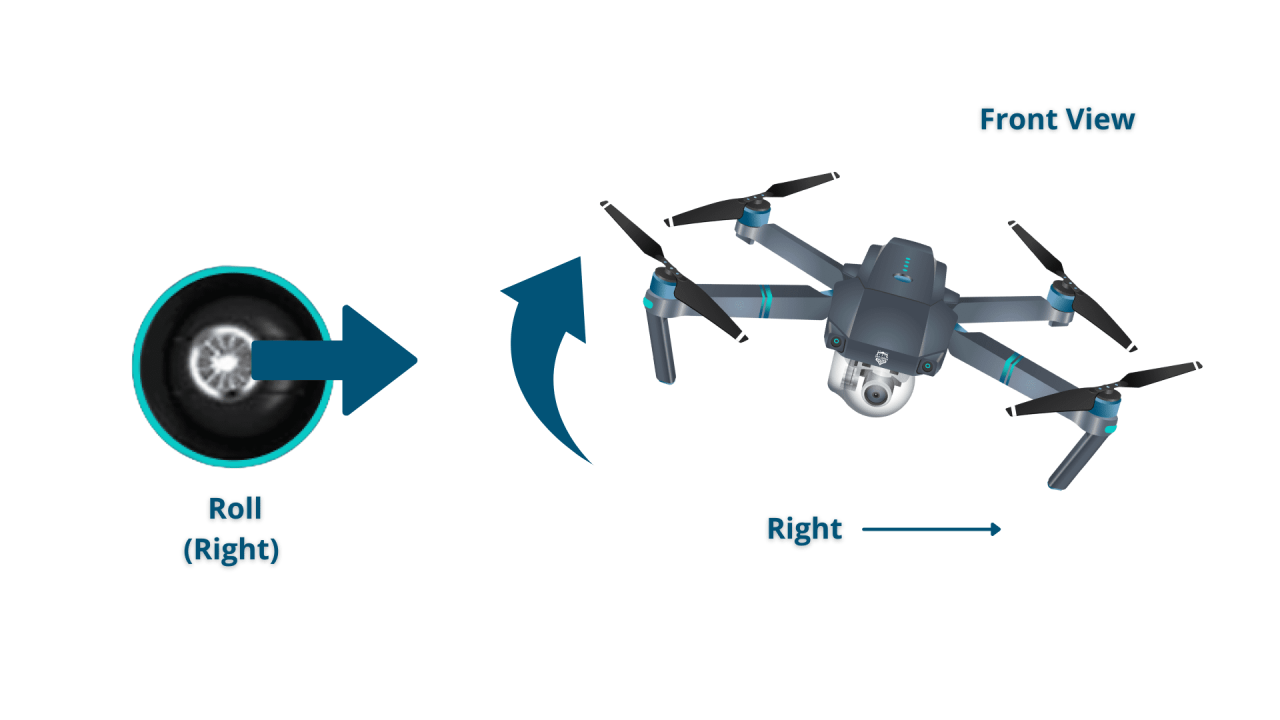
Most drone remotes feature two control sticks and several buttons. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls roll (tilt) and pitch (forward/backward movement). Buttons often control functions such as camera operation, return-to-home, and emergency stops. A visual diagram would clearly show the layout of these controls and their corresponding effects on the drone’s movement.
For example, pushing the left stick upwards increases altitude, while pushing it to the left initiates a counter-clockwise yaw. The right stick controls the drone’s pitch and roll. Pushing it forward causes the drone to move forward, and pushing it right initiates a rightward roll.
Drone Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration are crucial for precise drone navigation and stability. This process ensures the drone’s internal sensors are correctly aligned with the Earth’s magnetic field and GPS satellites.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Ensure the drone is in an open area, away from magnetic interference (metal objects, power lines).
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass calibration. This usually involves rotating the drone 360 degrees horizontally.
- For GPS calibration, allow the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal. This may take several minutes.
- Once calibration is complete, test the drone’s functionality in a safe environment.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, making them suitable for different tasks. GPS mode offers stability and automated features, while Attitude mode provides more direct control but requires more skill.
| Flight Mode | Description | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Maintains position and altitude using GPS. | Stable filming, beginners. |
| Attitude Mode | Controls drone based on stick inputs regardless of GPS. | Acrobatic maneuvers, experienced users. |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) | Drone automatically returns to its takeoff point. | Safety feature, battery low. |
| Sport Mode | Increased responsiveness and speed. | Experienced users in open areas. |
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing the Drone
Safe and efficient takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are essential for preventing accidents and ensuring the longevity of your drone.
Safe Drone Takeoff Procedure
A smooth and controlled takeoff minimizes the risk of collisions or damage.
- Perform a pre-flight check.
- Ensure sufficient space and clear airspace.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition.
- Slowly and gently lift the drone off the ground using the control stick.
- Maintain a steady ascent.
Maintaining Stable Flight and Precise Maneuvering
Stable flight and precise maneuvering require practice and understanding of the drone’s controls. Different techniques offer various advantages and disadvantages depending on the situation.
| Maneuvering Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Smooth Stick Inputs | Precise control, minimal oscillations. | Slower response time. |
| Short, Precise Movements | Quick adjustments, effective in tight spaces. | Potential for jerky movements. |
| Using Trim Adjustments | Corrects minor drifts, maintains stable hover. | Requires understanding of trim function. |
Safe and Controlled Landing Procedure
A safe landing procedure minimizes the risk of damage to the drone or surrounding environment.
- Select a suitable landing area, free of obstacles and hazards.
- Gradually descend the drone, maintaining a steady rate.
- Hover briefly just above the ground before gently setting it down.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Potential landing hazards include uneven terrain, obstacles (trees, wires), and strong winds. Mitigation strategies include selecting a flat, clear landing zone, carefully assessing wind conditions, and practicing controlled landings in various conditions.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial shots. This section covers essential aspects of drone photography.
Understanding Camera Settings
Aperture, shutter speed, and ISO are key camera settings that significantly impact image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO determines image sensitivity to light. Understanding the interplay of these settings allows for precise control over the final image. For example, a wide aperture (low f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background and emphasizing the subject.
A fast shutter speed (high value) freezes motion, while a slow shutter speed can create motion blur.
Aerial Shot Composition
Effective aerial shots require careful consideration of framing, perspective, and composition. A well-composed shot effectively conveys the scene’s essence. A poorly composed shot can appear cluttered and lack visual interest. For example, a well-composed shot might use the rule of thirds, placing the main subject off-center to create a more dynamic and engaging image. A poorly composed shot might have the main subject directly in the center, making it appear static and uninteresting.
Drone Footage and Photograph Management
An organized workflow is essential for efficient post-processing and archiving of drone footage and photographs. This involves creating a structured file system, using descriptive file names, and backing up your data regularly.
- Download footage and photos to a computer.
- Create a folder structure for organizing files by date and location.
- Use descriptive file names (e.g., Date_Location_Description).
- Back up your data to multiple locations.
Battery Management and Flight Time Optimization
Proper battery care and flight planning are crucial for maximizing flight time and extending the lifespan of your drone’s battery.
Proper Battery Care and Maintenance, How to operate a drone

Proper battery care is vital for extending its lifespan and ensuring safe operation. This involves storing batteries in a cool, dry place, avoiding overcharging or deep discharging, and regularly checking for damage.
Maximizing Flight Time
Flight planning and power management techniques are essential for extending flight duration. This includes optimizing flight routes, avoiding unnecessary maneuvers, and utilizing power-saving modes when possible.
Comparison of Battery Types
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics in terms of capacity, weight, and discharge rate. Choosing the right battery type is essential for optimizing flight time and performance.
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Weight (g) | Discharge Rate (C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 1500mAh | 1500 | 150 | 30C |
| LiPo 4S 2200mAh | 2200 | 220 | 45C |
| LiHV 3S 1800mAh | 1800 | 160 | 40C |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their solutions is crucial for efficient troubleshooting and minimizing downtime.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Various issues can arise during drone operation, ranging from minor glitches to major malfunctions. Quick identification and resolution are key to maintaining operational efficiency.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, damaged power switch. | Charge battery, replace battery, check power switch. |
| GPS signal lost | Weak signal, interference, faulty GPS module. | Move to an open area, recalibrate GPS, contact manufacturer. |
| Drone is unresponsive | Low battery, controller malfunction, interference. | Check battery, restart controller, check for interference. |
| Propeller malfunction | Damaged propeller, loose propeller, motor failure. | Replace propeller, tighten propeller, contact manufacturer. |
Drone Connection Loss
Losing connection with the controller can be a serious issue. Immediate action is necessary to recover the drone or minimize potential damage. This typically involves attempting to re-establish connection, initiating a Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available, or contacting relevant authorities if the drone is lost.
Basic Drone Maintenance and Repairs
Regular maintenance and minor repairs can extend the lifespan of your drone and prevent costly repairs. This includes cleaning the drone, checking for loose parts, and lubricating moving components.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly requires adherence to local, regional, and national regulations. This section Artikels essential legal considerations.
Essential Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary depending on location. It’s crucial to be aware of these regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure safe operation.
Learning to fly a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which you can easily do by checking out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Mastering these fundamentals will allow you to confidently and safely navigate the skies with your new drone, ensuring both successful flights and adherence to regulations.
- Registration requirements (may vary by country/region).
- Airspace restrictions (no-fly zones near airports, etc.).
- Weight limits for drones requiring registration or permits.
- Operating altitude restrictions.
- Rules regarding night flying.
- Privacy laws regarding data collection and image capture.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Certain drone operations may require permits or licenses. This is particularly true for commercial operations or flights in restricted airspace. Failure to obtain necessary permits can lead to fines or legal action.
Airspace Restrictions and Restricted Areas
Before each flight, it’s essential to check for airspace restrictions and restricted areas. Many online resources and mobile apps provide up-to-date information on airspace restrictions. Flying in restricted airspace is illegal and can be dangerous.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technological skill with responsible decision-making. By diligently following the pre-flight checklists, understanding the intricacies of drone controls, and adhering to safety regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember that continuous practice and a commitment to safe flying habits are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
This guide provides a solid foundation; however, remember to always consult official regulations and best practices specific to your region and continue learning to expand your skills and knowledge.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, obstacle avoidance, and automatic return-to-home functionality. Research reviews to find a model that suits your budget and needs.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning how to safely and effectively control the drone itself, which is thoroughly covered in this excellent guide on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, proficient drone piloting requires consistent practice and a deep understanding of both the technology and the legal framework surrounding its use.
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant interference.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If it doesn’t work, try to visually locate the drone and recover it safely. Check your controller’s batteries and ensure there are no obstructions interfering with the signal.
How do I store my drone batteries properly?
Store drone batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or heat sources. Store them at around 50% charge to prolong their lifespan. Never leave them charging unattended.
